2023CCPC 国赛(哈尔滨)题解
The 9th CCPC (Harbin) Onsite(The 2nd Universal Cup. Stage 10: Harbin)
B - Memory
Question
给定一个数组
Solution
很显然,如果用 double 暴力枚举的话会产生精度问题,这里我发现
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
int main() {
freopen ("B.in", "r", stdin);
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0); std::cout.tie(0);
int n; std::cin >> n;
int flg = 0;
size_t now_up = 0, now_dn = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x; std::cin >> x;
if (x > 0) now_up += x;
if (x < 0) now_dn += -x;
if (now_up == now_dn) {
if (flg == 0) std::cout << '0';
if (flg == 1) std::cout << '+';
if (flg == -1) std::cout << '-';
}
if (now_up > now_dn)
std::cout << '+';
if (now_dn > now_up)
std::cout << '-';
if ((now_dn & 1) ^ (now_up & 1)) {
if (now_dn & 1) flg = -1;
if (now_up & 1) flg = 1;
}
now_dn >>= 1; now_up >>= 1;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
D - A Simple MST Problem (数论,最小生成树,银牌题)
Question
定义
Solution
很显然有
根据贪心的想法,我们需要找边权非常小的点,那么就是
然后考虑边权为
由于一个
这里当时我不知道怎么处理,然后看了别人代码,发现可以记录下质因子集合的乘积,因为质因子集合和乘积是一一对应的,我们记在我之前的离我最近的质因子集合的乘积的下标为
我们只需要对
如果区间中不存在
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
struct DSU {
std::vector<int> f;
std::vector<int> size;
DSU(int n) : f(n), size(n) {
std::iota(f.begin(), f.end(), 0);
std::fill(size.begin(), size.end(), 1);
}
int find(int x) { // 路径压缩
while (x != f[x])
x = f[x] = f[f[x]];
return x;
}
void Union(int x, int y) {
if (find(x) == find(y))
return;
if (size[x] < size[y]) // 按秩合并
std::swap(x, y);
size[find(x)] += size[find(y)];
f[find(y)] = find(x);
}
};
constexpr int N = 1e6 + 5;
constexpr int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int P[N], w[N], proP[N], v[N], tot;
int L[N], R[N], cnt[N];
void init() {
v[1] = 1;
std::fill(proP, proP + N, 1);
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
if (v[i] == 0) {
P[++tot] = i;
v[i] = i; w[i] = 1;
proP[i] = i;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= tot && i * P[j] < N; j++) {
v[i * P[j]] = P[j];
if (i % P[j] == 0) {
w[i * P[j]] = w[i];
proP[i * P[j]] = proP[i];
break;
}
w[i * P[j]] = w[i] + 1;
proP[i * P[j]] = proP[i] * P[j];
}
}
auto find_div = [&] (int x) {
std::vector<int> res(1, 1);
while (x > 1) {
int d = v[x];
x /= d;
for (int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
res.push_back(res[i] * d);
}
return res;
};
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
auto divs = find_div(proP[i]);
for (int d : divs)
L[i] = std::max(L[i], cnt[d]);
cnt[proP[i]] = i;
}
std::fill(cnt, cnt + N, INF);
std::fill(R, R + N, INF);
for (int i = N - 1; i; i--) {
auto divs = find_div(proP[i]);
for (int d : divs)
R[i] = std::min(R[i], cnt[d]);
cnt[proP[i]] = i;
}
}
void cpSortarray<int, 3>> &a {
int M = 0;
for (const auto &[w, x, y] : a) M = std::max(M, w);
std::vector<std::vector<int>> cnt(M + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
cnt[a[i][0]].push_back(i);
std::vector<std::array<int, 3>> res;
for (int x = 0; x <= M; x++)
for (auto i : cnt[x])
res.push_back(a[i]);
a = res;
}
int mstarray<int, 3>> &e, int l, int r {
DSU dsu(r - l + 1);
cpSort(e);
int ret = 0;
for (const auto &[w, x, y] : e) {
if (dsu.find(x - l) != dsu.find(y - l)) {
dsu.Union(x - l, y - l);
ret += w;
}
}
return ret;
}
int edge(int x, int y) {
return w[x] + w[y] - w[std::gcd(x, y)];
}
void solve() {
int l, r; std::cin >> l >> r;
int ans = std::accumulate(w + l, w + r + 1, 0);
if (l == 1) {
std::cout << ans << '\n';
return;
}
std::vector<std::array<int, 3>> e;
int prime = 0;
for (int x = l; x <= r; x++) {
if (w[x] == 1)
prime = x;
}
if (prime == 0) {// 区间内没有 w[x]=1 的数
for (int i = l; i < r; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j <= r; j++)
e.push_back({edge(i, j), i, j});
ans = mst(e, l, r);
std::cout << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
for (int x = l; x <= r; x++) {
if (L[x] >= l)
e.push_back({w[x], x, L[x]});
if (R[x] <= r)
e.push_back({w[x], x, R[x]});
if (prime != x)
e.push_back({edge(x, prime), x, prime});
}
ans = mst(e, l, r);
std::cout << ans << '\n';
}
int main() {
freopen ("D.in", "r", stdin);
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(NULL); std::cout.tie(NULL);
init();
int _; std::cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
Summary
当值域特别小时,可以考虑用桶排序
这里在求一个数的因子的时候,用了一种比较特殊的办法,用欧拉筛维护了一个
auto find_div = [&] (int x) {
std::vector<int> res(1, 1);
while (x > 1) {
int d = v[x];
x /= d;
for (int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
res.push_back(res[i] * d);
}
return res;
};
时间复杂度要优于
G - The Only Way to the Destination (图论, 铜牌题)
Quesiton
给定一个
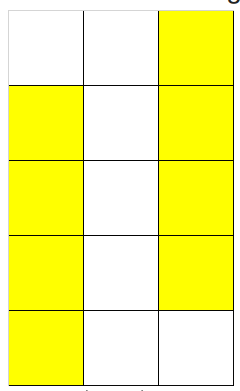
Solution
由于 NO,所以本质上
假设我们对每个空格子都上下左右建边,只需要判断是否存在环即可
但是
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
struct Wall {
int x1, x2, y, id;
};
int main() {
freopen ("G.in", "r", stdin);
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(NULL); std::cout.tie(NULL);
int n, m, k; std::cin >> n >> m >> k;
std::vector<Wall> walls(k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
std::cin >> walls[i].x1 >> walls[i].x2 >> walls[i].y;
}
std::sort(walls.begin(), walls.end(), [&](const Wall &a, const Wall &b) {
return a.y < b.y || (a.y == b.y && a.x1 < b.x1);
});
if (n == 1) {
int l = 0, r = k - 1;
while (l < k && walls[l].y == l + 1) l += 1;
while (r >= 0 && walls[r].y == m - (k - 1 - r)) r -= 1;
std::cout << (l > r ? "YES" : "NO") << '\n';
return 0;
}
int cnt = 0, pos = 0;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> g(10 * k);
auto add_e = [&] (int u, int v) {
g[u].push_back(v); g[v].push_back(u);
};
std::vector<Wall> v, pre_v;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { // 枚举列
pre_v = v; v.clear();
while (pos < k && walls[pos].y == i) {
if (pos == 0 || walls[pos].y != walls[pos - 1].y) {
if (walls[pos].x1 > 1)
v.push_back({1, walls[pos].x1 - 1, i, ++cnt});
}
else {
if (walls[pos - 1].x2 + 1 <= walls[pos].x1 - 1)
v.push_back({walls[pos - 1].x2 + 1, walls[pos].x1 - 1, i, ++cnt});
}
pos += 1;
}
if (pos == 0 || walls[pos - 1].y != i) {
if (pre_v.size() == 1 && pre_v.back().x1 == 1 && pre_v.back().x2 == n) {
std::cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
v.push_back({1, n, i, ++cnt});
}
else if (walls[pos - 1].x2 < n) {
v.push_back({walls[pos - 1].x2 + 1, n, i, ++cnt});
}
for (int pre_j = 0, j = 0; pre_j < pre_v.size(); pre_j++) {
while (j < v.size() && v[j].x2 < pre_v[pre_j].x1) j += 1;
while (j < v.size() && v[j].x1 <= pre_v[pre_j].x2) { // 相交
int L = std::max(v[j].x1, pre_v[pre_j].x1), R = std::min(v[j].x2, pre_v[pre_j].x2);
if (R ^ L) {
std::cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
add_e(v[j].id, pre_v[pre_j].id);
if (v[j].x2 > pre_v[pre_j].x2) break;
j += 1;
}
}
}
g.resize(cnt + 1);
if (cnt == 1) {
std::cout << "YES" << "\n";
return 0;
}
std::vector<int> du(cnt + 1, 0);
int num = 0; std::queue<int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) du[i] = g[i].size();
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) if (du[i] == 1)
q.push(i), num += 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto v : g[u]) {
if (--du[v] == 1) {
q.push(v); num += 1;
}
}
}
std::cout << (num == cnt ? "YES" : "NO") << '\n';
return 0;
}
H - Energy Distribution (高斯消元, 银牌题)
Question
给出一个
的最大值
Solution
枚举
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using ld = double;
constexpr ld eps = 1e-9;
int sgn(const ld &a) {
if (a < -eps)
return -1;
return (a > eps);
}
std::string gaussvector<ld>> &a { // 传入增广矩阵
int n = a.size();
int c = 0, r = 0;
for (c = 0, r = 0; c < n; c++) {
int tmp = r;
for (int i = r; i < n; i++)
if (sgn(a[i][c]))
tmp = i;
if (sgn(a[tmp][c]) == 0)
continue;
std::swap(a[tmp], a[r]);
for (int i = n; i >= c; i--)
a[r][i] /= a[r][c];
for (int i = r + 1; i < n; i++)
if (sgn(a[i][c]))
for (int j = n; j >= c; j--)
a[i][j] -= a[r][j] * a[i][c];
r += 1;
}
if (r < n) {
for (int i = r; i < n; i++)
if (sgn(a[i][n]))
return "NoSolution";
return "InfSolution";
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
a[i][n] -= a[j][n] * a[i][j];
return "OK";
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr); std::cout.tie(nullptr);
int n; std::cin >> n;
std::vector w(n, std::vector<int>(n , 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
std::cin >> w[i][j];
ld ans = 0;
for (int S = 1; S < (1 << n); S++) {
int m = __builtin_popcount((S));
if (m <= 1)
continue;
std::vector a(m, std::vector<ld>(m + 1, 0));
std::vector<int> b;
for (int T = S; T ; T -= T & -T) {
b.push_back__lg(T & -T);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
a[0][i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++)
a[j][k] = w[b[j]][b[k]] - w[b[j - 1]][b[k]];
}
auto res = gauss(a);
if (res == "OK") {
ld now = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
if (sgn(a[i][m]) == -1)
now = -1e9;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < m; j++)
now += a[i][m] * a[j][m] * w[b[i]][b[j]];
ans = std::max(ans, now);
}
}
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(10) << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
J - Game on a Forest (SG函数,铜牌题)
Question
给出一个森林,Plover和Georgia轮流对图进行操作,Georgia先手,操作是两种类型之一
- 选择图中的一条边,然后移除它。
- 选择图中的一个节点,然后移除该节点以及与其相连的边。
第一个无法操作的人失败,求 Georgia 有多少种不同的必胜的第一次操作
Solution
博弈问题考虑 SG 函数,通过归纳我们可以发现,对于一颗树来说,节点个数为奇数,
总体的
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
int main() {
freopen ("J.in", "r", stdin);
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(NULL); std::cout.tie(NULL);
int n, m; std::cin >> n >> m;
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> edges;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> g(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int u, v; std::cin >> u >> v;
edges.push_back({u, v});
g[u].push_back(v); g[v].push_back(u);
}
std::function<int(int)> sg = [&](int u) {
if (u == 0) return 0;
if (u & 1) return 1;
else return 2;
};
std::vector<int> from(n + 1, 0), siz(n + 1, 0);
std::function<void(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int u, int fa, int frm) {
from[u] = frm;
siz[u] = 1;
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (v == fa) continue;
dfs(v, u, frm);
siz[u] += siz[v];
}
};
int cnt = 0, SG = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (siz[i] == 0) {
dfs(i, 0, i); cnt += 1;
SG = SG ^ sg(siz[i]);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int now_sg = SG ^ sg(siz[from[i]]);
for (auto v : g[i]) {
if (siz[v] > siz[i]) continue;
now_sg = now_sg ^ sg(siz[v]);
}
now_sg = now_sg ^ sg(siz[from[i]] - siz[i]);
if (now_sg == 0) ans += 1;
}
for (auto [u, v] : edges) {
int now_sg = SG ^ sg(siz[from[u]]);
int siz_ = std::min(siz[u], siz[v]);
now_sg ^= sg(siz_); now_sg ^= sg(siz[from[u]] - siz_);
if (now_sg == 0) ans += 1;
}
std::cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
L- Palm Island
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int ll;
ll Tex, n, x;
vector<ll> a, b;
void f(vector<ll> & qwq, vector<ll> & p){
for(auto &it : p){
qwq.push_back(it);
}
p.clear();
}
void AC(){
cin >> n;
a.clear(); b.clear();
a.push_back(0);
b.push_back(0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
cin >> x;
a.push_back(x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
cin >> x;
b.push_back(x);
}
vector<ll> q1, q2, q3, q4;
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i --){
if(b[i] == a[i]) continue;
ll idx;
for(int j = 1; j < i; j ++){
if(a[j] == b[i]) idx = j;
}
// cout << " " << i << "\n";
q1.clear(); q2.clear(); q3.clear(); q4.clear();
q4.push_back(b[i]);
if(idx - 1 > 0){
for(int k = 1; k < idx; k ++){
q1.push_back(a[k]);
}
}
if(i - idx > 0){
for(int k = idx + 1; k <= i; k ++){
q2.push_back(a[k]);
}
}
if(n - i > 0){
for(int k = i + 1; k <= n; k ++){
q3.push_back(a[k]);
}
}
if(i == n){
if(idx > 0) cout << string(idx, '1');
a.clear(); a.push_back(0);
if(q2.size()) f(a, q2);
if(q1.size()) f(a, q1);
if(q4.size()) f(a, q4);
}
else{
if(idx - 1 > 0) cout << string(idx - 1, '1');
if(i - idx > 0) cout << string(i - idx, '2');
if(n - i + 1 > 0) cout << string(n - i + 1, '1');
a.clear(); a.push_back(0);
if(q1.size()) f(a, q1);
if(q2.size()) f(a, q2);
if(q4.size()) f(a, q4);
if(q3.size()) f(a, q3);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
freopen ("L.in", "r", stdin);
freopen ("L.out", "w", stdout);
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> Tex;
while(Tex --) AC();
return 0;
}
M - Painter
Solution
队友写的签到
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
struct node{
string id;
ll x1, y1, x2, y2, r;
char ch;
};
ll n;
vector<node> a;
bool check1(ll x, ll y, ll r, ll x0, ll y0){
return (x0 - x) * (x0 - x) + (y0 - y) * (y0 - y) <= r * r;
}
bool check2(ll x1, ll y1, ll x2, ll y2, ll x0, ll y0){
return (x1 <= x0) && (x0 <= x2) && (y1 <= y0) && (y0 <= y2);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
string opt;
ll x1, y1, x2, y2, r;
char ch;
cin >> opt;
if(opt == "Circle"){
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> r >> ch;
a.push_back({opt, x1, y1, 0, 0, r, ch});
}
else if(opt == "Rectangle"){
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> ch;
a.push_back({opt, x1, y1, x2, y2, 0, ch});
}
else{
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
for(int j = y2; j >= y1; j --){
for(int i = x1; i <= x2; i ++){
// cout << i << " " << j << "\n";
char ans = '.';
for(int k = a.size() - 1; k >= 0; k --){
if(a[k].id == "Circle"){
if(check1(a[k].x1, a[k].y1, a[k].r, i, j)){
ans = a[k].ch;
break;
}
}
else{
if(check2(a[k].x1, a[k].y1, a[k].x2, a[k].y2, i, j)){
ans = a[k].ch;
break;
}
}
}
cout << ans;
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
}
return 0;
}